Mitochondrion: Difference between revisions
Notjusttired (talk | contribs) (move refs to notable studies, fix Arnand vol no) |
Notjusttired (talk | contribs) (→Notable studies: tidy, del duplicates) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Notable studies== | ==Notable studies== | ||
* 1991, Mitochondrial abnormalities in the postviral fatigue syndrome<ref name="Behan1991">{{citation | * 1991, Mitochondrial abnormalities in the postviral fatigue syndrome<ref name="Behan1991">{{citation | ||
| last1 = Behan | first1 = WMH | authorlink1 = Wilhelmina Behan | | last1 = Behan | first1 = WMH | authorlink1 = Wilhelmina Behan | ||
| Line 59: | Line 58: | ||
| url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7633428 | | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7633428 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
*1996, Sensory characterization of somatic parietal tissues in humans with chronic fatigue syndrome<ref name="Vecchiet1996">{{citation | |||
* | |||
| last1 = Vecchiet | first1 = L | | last1 = Vecchiet | first1 = L | ||
| last2 = Montanari | first2 = G | | last2 = Montanari | first2 = G | ||
| Line 161: | Line 74: | ||
| url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8859904 | | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8859904 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
*2009, <ref name="Saric2009">{{citation | * 1997, [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9149090 Chronic fatigue syndrome and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function]<ref name=Lodi1997>{{Cite journal|last=Lodi|first=R.|last2=Taylor|first2=D. J.|last3=Radda|first3=G. K.|date=1997|title=Chronic fatigue syndrome and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9149090|journal=Muscle & Nerve|volume=20|issue=6|pages=765–766|issn=0148-639X|pmid=9149090|via=}}</ref> | ||
* 2005, Targeting of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF to host mitochondria is essential for bacterial pathogenesis: critical role of the 16th leucine residue in EspF<ref name="Nagai2005">{{Citation | |||
| last1 = Nagai | first1 = T | authorlink1 = T Nagai | |||
| last2 = Abe | first2 = A | authorlink2 = A Abe | |||
| last3 = Sasakawa | first3 = C | authorlink3 = C Sasakawa | |||
| display-authors = | |||
| title = Targeting of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF to host mitochondria is essential for bacterial pathogenesis: critical role of the 16th leucine residue in EspF | |||
| journal = J Bio. Chem. | volume = | issue = | page = | |||
| date = January 2005 | |||
| pmid = 15533930 | |||
| doi = 10.1074/jbc.M411550200 | |||
}} | |||
</ref> | |||
*2009, Chronic fatigue syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction<ref name="Myhill2009">{{citation | |||
| last1 = Myhill | first1 = S | authorlink1 = Sarah Myhill | |||
| last2 = Booth | first2 = NE | authorlink2 = Norman Booth | |||
| last3 = McLaren-Howard | first3 = J | authorlink3 = John McLaren-Howard | |||
| title = Chronic fatigue syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction | |||
| journal = Int J Clin Exp Med | volume = 2| issue = 1| pages = 1–16 | |||
| date = 15 Jan 2009 | |||
| pmid = 19436827 | |||
| url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2680051/ | |||
}}</ref> | |||
*2009, Integrated cytokine and metabolic analysis of pathological responses to parasite exposure in rodents<ref name="Saric2009">{{citation | |||
| last1 = Saric | first1 = J | | last1 = Saric | first1 = J | ||
| last2 = Li | first2 = JV | | last2 = Li | first2 = JV | ||
| Line 174: | Line 110: | ||
| url = http://http://doi.org/10.1021/pr901019z | | url = http://http://doi.org/10.1021/pr901019z | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
* | *2009, Coenzyme Q10 deficiency in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is related to fatigue, autonomic and neurocognitive symptoms and is another risk factor explaining the early mortality in ME/CFS due to cardiovascular disorder<ref name="Maes2009">{{Citation | ||
| last1 = | | last1 = Maes | first1 = M | authorlink1 = Michael Maes | ||
| last2 = | | last2 = Mihaylova | first2 = I | authorlink2 = Ivanka Mihaylova | ||
| last3 = | | last3 = Kubera | first3 = M | authorlink3 = Marta Kubera | ||
| last4 = | | last4 = Uytterhoeven | first4 = M | authorlink4 = Marc Uytterhoeven | ||
| last5 = Vrydags | first5 = N | authorlink5 = Nicholas Vrydags | |||
| last6 = Bosmans | first6 = E | authorlink6 = Eugene Bosmans | |||
| display-authors = | | display-authors = | ||
| title = | | title = Coenzyme Q10 deficiency in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is related to fatigue, autonomic and neurocognitive symptoms and is another risk factor explaining the early mortality in ME/CFS due to cardiovascular disorder | ||
| journal = Neuro Endocrinol Lett. | volume = | issue = | page = | |||
| date = 2009 | |||
| pmid = 20010505 | |||
| journal = | |||
| date = | |||
| pmid = | |||
| doi = | | doi = | ||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*2010, <ref name="Vermeulen2010">{{Citation | *2010, Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome performed worse than controls in a controlled repeated exercise study despite a normal oxidative phosphorylation capacity<ref name="Vermeulen2010">{{Citation | ||
| last1 = Vermeulen | first1 = RC | authorlink1 = RC Vermeulen | | last1 = Vermeulen | first1 = RC | authorlink1 = RC Vermeulen | ||
| last2 = Kirk | first2 = RM | authorlink2 = RM Kirk | | last2 = Kirk | first2 = RM | authorlink2 = RM Kirk | ||
| Line 215: | Line 139: | ||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
* | * 2010, Interactions between bacterial pathogens and mitochondrial cell death pathways<ref name="Rudel2010">{{Citation | ||
| last1 = | | last1 = Rudel T | first1 = T | authorlink1 = T Rudel | ||
| last2 = | | last2 = Kepp O | first2 = O | authorlink2 = O Kepp | ||
| last3 = | | last3 = Kozjak-Pavlovic V | first3 = V | authorlink3 = V Kozjak-Pavlovic | ||
| | | display-authors = | ||
| | | title = Interactions between bacterial pathogens and mitochondrial cell death pathways | ||
| | | journal = Nat Rev Microbiol. | volume = | issue = | page = | ||
| date = October 2010 | |||
| pmid = 20818415 | |||
| doi = 10.1038/nrmicro2421 | |||
}} | |||
</ref> | |||
*2012, Mitochondrial dysfunction and the pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)<ref name="Booth2012">{{citation | |||
| last1 = Booth | first1 = NE | authorlink1 = Norman Booth | |||
| last2 = Myhill | first2 = S | authorlink2 = Sarah Myhill | |||
| last3 = McLaren-Howard | first3 = J | authorlink3 = John McLaren-Howard | |||
| title = Mitochondrial dysfunction and the pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) | |||
| journal = Int J Clin Exp Med | volume = 5| issue = 3| pages = 208–220 | |||
| date = 2012 | |||
| pmid = 22837795 | |||
| url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22837795 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
*2013, Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) - a clinical audit<ref name="Myhill2013">{{Citation | |||
| last1 = Myhill | first1 = Sarah | authorlink1 = Sarah Myhill | |||
| last2 = Booth | first2 = Norman E| authorlink2 = Norman Booth | |||
| last3 = McLaren-Howard | first3 = John | authorlink3 = John McLaren-Howard | |||
| display-authors = | | display-authors = | ||
| title = | | title = Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) - a clinical audit. | ||
| journal = | | journal = International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine | volume = | issue = | page = | ||
| date = | | date = 2013 | ||
| pmid = | | pmid = 23236553 | ||
| doi = | | doi = | ||
| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3515971/ | |||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*2013, <ref name="Morris2013">{{Citation | *2013, Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and encephalomyelitis disseminata/multiple sclerosis show remarkable levels of similarity in phenomenology and neuroimmune characteristics.<ref name="Morris2013">{{Citation | ||
| last1 = Morris | first1 = G | authorlink1 = Gerwyn Morris | | last1 = Morris | first1 = G | authorlink1 = Gerwyn Morris | ||
| last2 = Maes | first2 = M | authorlink2 = Michael Maes | | last2 = Maes | first2 = M | authorlink2 = Michael Maes | ||
| Line 241: | Line 185: | ||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*2014, <ref name="Morris2014">{{Citation | *2013, [http://www.hindawi.com/journals/av/2013/738794/abs/ Viruses as Modulators of Mitochondrial Functions]<ref name="Anand2013">{{citation | ||
| last1 = Anand | first1 = Sanjeev K | authorlink1 = Sanjeev Anand | |||
| last2 = Tikoo | first2 = Suresh K | authorlink2 = Suresh Tikoo | |||
| title = Viruses as Modulators of Mitochondrial Functions | |||
| journal = Advances in Virology, Advances in Virology | volume = 2013| pages = 738794 | |||
| date = 2013-10-24 | |||
| doi = 10.1155/2013/738794 | |||
| url = http://www.hindawi.com/journals/av/2013/738794/abs/ | |||
}}</ref> | |||
* 2013, The role of mitochondrial dysfunctions due to oxidative and nitrosative stress in the chronic pain or chronic fatigue syndromes and fibromyalgia patients: peripheral and central mechanisms as therapeutic targets?<ref name="Meeus2013">{{Citation| last1 = Meeus | first1 = M | authorlink1 = Mira Meeus| last2 = Nijs | first2 = J | authorlink2 = Jo Nijs| last3 = Hermans | first3 = L | authorlink3 = | last4 = Goubert | first4 = D | authorlink4 = | last5 = Calders | first5 = P | authorlink5 = | display-authors = | |||
| title = The role of mitochondrial dysfunctions due to oxidative and nitrosative stress in the chronic pain or chronic fatigue syndromes and fibromyalgia patients: peripheral and central mechanisms as therapeutic targets? | |||
| journal = Expert Opin Ther Targets | volume = | issue = | page = | |||
| date = September 2013 | pmid = 23834645 | doi = 10.1517/14728222.2013.818657 | |||
}} | |||
</ref> | |||
* 2014, Metabolism in chronic fatigue syndrome<ref name="Armstrong2014">{{Citation | |||
| last1 = Armstrong | first1 = CW | authorlink1 = Christopher Armstrong | |||
| last2 = McGregor | first2 = NR | authorlink2 = Neil McGregor | |||
| last3 = Butt | first3 = HL | authorlink3 = Henry Butt | |||
| last4 = Gooley | first4 = PR | authorlink4 = Paul Gooley | |||
| display-authors = | |||
| title = Metabolism in chronic fatigue syndrome | |||
| journal = Adv Clin Chem | volume = 66 | issue = | page = 121-72 | |||
| date = Oct 2014 | |||
| pmid = 25344988 | |||
| doi = 10.1016/B978-0-12-801401-1.00005-0 | |||
| url = http://www.academia.edu/11578244/CHAPTER_FIVE_Metabolism_in_Chronic_Fatigue_Syndrome | |||
}}</ref> | |||
*2014, Mitochondrial dysfunctions in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome explained by activated immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways<ref name="Morris2014">{{Citation | |||
| last1 = Morris | first1 = Gerwyn | authorlink1 = Gerwyn Morris | | last1 = Morris | first1 = Gerwyn | authorlink1 = Gerwyn Morris | ||
| last2 = Maes | first2 = Michael | authorlink2 = Michael Maes | | last2 = Maes | first2 = Michael | authorlink2 = Michael Maes | ||
| Line 252: | Line 224: | ||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
* | *2015, Mitoprotective dietary approaches for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Caloric restriction, fasting, and ketogenic diets<ref name="Craig2015">{{citation | ||
| last1 = | | last1 = Craig | first1 = Courtney | authorlink1 = Courtney Craig | ||
| last2 = | | title = Mitoprotective dietary approaches for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Caloric restriction, fasting, and ketogenic diets | ||
| last3 = | | journal = Medical Hypotheses | volume = 85 | issue = 5 | page = 690-693 | ||
| display-authors = | | date = Nov 2015 | ||
| title = | | pmid = 26315446 | ||
| journal = | | doi = 10.1016/j.mehy.2015.08.013 | ||
| date = | | url = http://www.medical-hypotheses.com/article/S0306-9877(15)00318-7/abstract | ||
| pmid = | }}</ref> | ||
| | *2015, Mitochondrial Myopathy in Follow-up of a Patient With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome<ref name="Galán2015">{{citation | ||
}} | | last1 = Galán | first1 = Fernando | authorlink1 = Galán Fernando | ||
</ref> | | last2 = de Lavera | first2 = Isabel | authorlink2 = Isabel de Lavera | ||
*2016, <ref name="Siu2016">{{Citation | | last3 = Cotán | first3 = David | authorlink3 = David Cotán | ||
| last4 = Sánchez-Alcázar | first4 = José A | authorlink4 = Sánchez-Alcázae | |||
| title = Mitochondrial Myopathy in Follow-up of a Patient With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome | |||
| journal = J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep | volume = 3| issue = 3 | |||
| date = 24 Sep 2015 | |||
| pmid = 26904705 | |||
| doi = 10.1177/2324709615607908 | |||
| url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4748504/ | |||
}}</ref> | |||
*2015, Increased prevalence of two mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in functional disease: Are we describing different parts of an energy-depleted elephant?<ref name="Boles2015">{{citation | |||
| last1 = Boles | first1 = RG | authorlink1 = Richard Boles | |||
| last2 = Zaki | first2 = EA | authorlink2 = Essam Zaki | |||
| last3 = Kerr | first3 = JR | authorlink3 = Jonathan Kerr | |||
| last4 = Das | first4 = K | authorlink4 = Kingshuk Das | |||
| last5 = Biswas | first5 = S | authorlink5 = Sawona Biswas | |||
| last6 = Gardner | first6 = A | authorlink6 = Ann Gardner | |||
| display-authors = 3 | |||
| title = Increased prevalence of two mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in functional disease: Are we describing different parts of an energy-depleted elephant? | |||
| journal = Mitochondrion | volume = 23 | page = 1-6 | |||
| date = Jul 2015 | |||
| pmid = 25934187 | doi = 10.1016/j.mito.2015.04.005 | |||
| url = http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567724915000483 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
* 2015, [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Neil_Mcgregor/publication/277979239_Metabolic_profiling_reveals_anomalous_energy_metabolism_and_oxidative_stress_pathways_in_chronic_fatigue_syndrome_patients/links/55aecf4408ae98e661a6f1eb/Metabolic-profiling-reveals-anomalous-energy-metabolism-and-oxidative-stress-pathways-in-chronic-fatigue-syndrome-patients.pdf Metabolic profiling reveals anomalous energy metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in chronic fatigue syndrome patients]<ref name=Armstrong2015>{{Cite journal|url= https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Neil_Mcgregor/publication/277979239_Metabolic_profiling_reveals_anomalous_energy_metabolism_and_oxidative_stress_pathways_in_chronic_fatigue_syndrome_patients/links/55aecf4408ae98e661a6f1eb/Metabolic-profiling-reveals-anomalous-energy-metabolism-and-oxidative-stress-pathways-in-chronic-fatigue-syndrome-patients.pdf |title=Metabolic profiling reveals anomalous energy metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in chronic fatigue syndrome patients|last=Armstrong|first=Christopher W.|author-link=Christopher Armstrong|last2=McGregor|first2=Neil R.|author-link2=Neil McGregor|date=May 22, 2015|journal= Metabolic profiling reveals anomalous energy metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in chronic fatigue syndrome patients|journal =Metabolomics|volume=11|pages =1626–1639|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=|last3=Lewis|first3=Donald P.|author-link3 =Donald P Lewis|last4=Butt|first4=Henry L.|last5=Gooley|first5=Paul R.}}</ref> | |||
* 2016, Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein cooperates with phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα to induce mitochondrial fragmentation<ref name="Siu2016">{{Citation | |||
| last1 = Siu | first1 = GK | authorlink1 = GK Siu | | last1 = Siu | first1 = GK | authorlink1 = GK Siu | ||
| last2 = Zhou | first2 = F | authorlink2 = F Zhou | | last2 = Zhou | first2 = F | authorlink2 = F Zhou | ||
| Line 282: | Line 278: | ||
}} | }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*2016, [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27389587 Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?]<ref name =Ostojic2016>{{Cite journal|last=Ostojic|first=Sergej M.|date=Aug 1, 2016|title=Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27389587|journal=Clinical Science (Lond.)|volume=130|issue=16|pages=1407–1416|doi=10.1042/CS20160200|issn=1470-8736|pmid=27389587|via=}}</ref> | *2016, [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27389587 Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?]<ref name =Ostojic2016>{{Cite journal|last=Ostojic|first=Sergej M.|date=Aug 1, 2016|title=Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27389587|journal=Clinical Science (Lond.)|volume=130|issue=16|pages=1407–1416|doi=10.1042/CS20160200|issn=1470-8736|pmid=27389587|via=}}</ref> | ||
*2016, [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25788480 Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts]<ref name=Felici2016>{{Cite journal|last=Felici|first=Roberta|last2=Lapucci|first2=Andrea|last3=Cavone|first3=Leonardo|last4=Pratesi|first4=Sara|last5=Berlinguer-Palmini|first5=Rolando|last6=Chiarugi|first6=Alberto|date=2015|title=Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25788480|journal=Molecular Pharmacology|volume=87|issue=6|pages=965–971|doi=10.1124/mol.114.097204|issn=1521-0111|pmid=25788480|via=}}</ref> | *2016, [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25788480 Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts]<ref name=Felici2016>{{Cite journal|last=Felici|first=Roberta|last2=Lapucci|first2=Andrea|last3=Cavone|first3=Leonardo|last4=Pratesi|first4=Sara|last5=Berlinguer-Palmini|first5=Rolando|last6=Chiarugi|first6=Alberto|date=2015|title=Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25788480|journal=Molecular Pharmacology|volume=87|issue=6|pages=965–971|doi=10.1124/mol.114.097204|issn=1521-0111|pmid=25788480|via=}}</ref> | ||
* | *2016, Mitochondrial DNA variants correlate with symptoms in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome<ref name="BillingRoss2016">{{citation | ||
| last1 = Billing-Ross | first1 = Paul | authorlink1 = Paul Billing-Ross | |||
| last2 = Germain | first2 = Arnaud | authorlink2 = Arnaud Germain | |||
| last3 = Ye | first3 = Kaixiong | authorlink3 = Kaixiong Ye | |||
| last4 = Keinan | first4 = Alon | authorlink4 = Alon Keinan | |||
| last5 = Gu | first5 = Zhenglong | authorlink5 = Zhenglong Gu | |||
| last6 = Hanson | first6 = Maureen R | authorlink6 = Maureen Hanson | |||
| display-authors = 3 | |||
| title = Mitochondrial DNA variants correlate with symptoms in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome | |||
| journal = Journal of Translational Medicine| issn = 1479-5876| volume = 14| pages = 19 | |||
| date = 2016 | |||
| pmid = 26791940 | doi = 10.1186/s12967-016-0771-6 | |||
| url = http://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-016-0771-6 | |||
| lay-url = http://hansonlab.org/research/cfs_me/mitochondria/ | |||
}}</ref> | |||
*2018, [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0448-9 Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation]<ref name=Sliter2018>{{Cite journal|last=Sliter|first=Danielle A.|last2=Martinez|first2=Jennifer|last3=Hao|first3=Ling|last4=Chen|first4=Xi|last5=Sun|first5=Nuo|last6=Fischer|first6=Tara D.|last7=Burman|first7=Jonathon L.|last8=Li|first8=Yan|last9=Zhang|first9=Zhe|date=2018-08-22|title=Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0448-9|journal=Nature|language=En|doi=10.1038/s41586-018-0448-9|issn=0028-0836}}</ref> | *2018, [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0448-9 Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation]<ref name=Sliter2018>{{Cite journal|last=Sliter|first=Danielle A.|last2=Martinez|first2=Jennifer|last3=Hao|first3=Ling|last4=Chen|first4=Xi|last5=Sun|first5=Nuo|last6=Fischer|first6=Tara D.|last7=Burman|first7=Jonathon L.|last8=Li|first8=Yan|last9=Zhang|first9=Zhe|date=2018-08-22|title=Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0448-9|journal=Nature|language=En|doi=10.1038/s41586-018-0448-9|issn=0028-0836}}</ref> | ||
*2020, Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome<ref name="Schreiner2020">{{Cite journal|last=Schreiner|first=Philipp|author-link=|last2=Harrer|first2=Thomas|author-link2=Thomas Harrer|last3=Scheibenbogen|first3=Carmen|author-link3=Carmen Scheibenbogen|last4=Lamer|first4=Stephanie|author-link4=|last5=Schlosser|first5=Andreas|author-link5=|last6=Naviaux|first6=Robert K.|author-link6=Robert Naviaux|last7=Prusty|first7=Bhupesh K.|author-link7=Bhupesh Prusty|last8=|first8=|date=2020-04-01|title=Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome|url=https://www.immunohorizons.org/content/4/4/201|journal=ImmunoHorizons|language=en|volume=4|issue=4|pages=201–215|doi=10.4049/immunohorizons.2000006|issn=2573-7732|pmc=|pmid=32327453|access-date=|quote=|via=}}</ref> [https://www.immunohorizons.org/content/4/4/201 (Full text)] | *2020, Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome<ref name="Schreiner2020">{{Cite journal|last=Schreiner|first=Philipp|author-link=|last2=Harrer|first2=Thomas|author-link2=Thomas Harrer|last3=Scheibenbogen|first3=Carmen|author-link3=Carmen Scheibenbogen|last4=Lamer|first4=Stephanie|author-link4=|last5=Schlosser|first5=Andreas|author-link5=|last6=Naviaux|first6=Robert K.|author-link6=Robert Naviaux|last7=Prusty|first7=Bhupesh K.|author-link7=Bhupesh Prusty|last8=|first8=|date=2020-04-01|title=Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome|url=https://www.immunohorizons.org/content/4/4/201|journal=ImmunoHorizons|language=en|volume=4|issue=4|pages=201–215|doi=10.4049/immunohorizons.2000006|issn=2573-7732|pmc=|pmid=32327453|access-date=|quote=|via=}}</ref> [https://www.immunohorizons.org/content/4/4/201 (Full text)] | ||
Revision as of 20:35, September 27, 2020
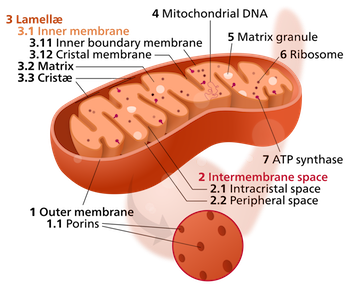
A mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is an organelle found in all cells that have a nucleus. In the human body, that would be all cells except red blood cells. Mitochondria generate most of a cell's energy by manufacturing adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Mitochondria have their own independent genome called mitochondrial DNA.
Biogenesis[edit | edit source]
Mitochondrial biogenesis (the creation of new mitochondria) can be increased via hormesis, the exposure of the body to short-term stressors. Healthy stressors include exercise, fasting, cold, heat and light. Resveratrol may also increase mitochondrial biogenesis.
Infection and immunity[edit | edit source]
Mitochondria play crucial role in innate immunity, namely through their induction of interferon production and apoptosis through mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS).[1] Many viruses, including Coxsackievirus B3, echovirus 7, and enterovirus 71 inhibit interferon induction and evade host immunity by cleaving or downregulating MAVS.[2]
Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1),[3] influenza virus,[3] and poliovirus[4] have all been found to reduce cellular respiration. Hepatitis C reduces aerobic metabolism and upregulates glycolysis.[5]
In human disease[edit | edit source]
Infection with pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites, can all induce changes in mitochondrial function and energy metabolism.
Viruses can induce or inhibit mitochondrial processes in order to replicate. "Viruses like Herpes simplex virus 1 deplete the host mitochondrial DNA and some, like human immunodeficiency virus and Hepatitis C Virus, hijack the host mitochondrial proteins to function fully inside the host cell."[6][7] Hepatitis C has also been shown to "fragment host mitochondria".[7]
Parasites such as toxoplasma gondii have also been shown to modulate host energy metabolism and dysregulate mitochondrial function,[8] as have bacteria[9] such as E. coli (Escherichia coli), which has been shown to modulate mitochondrial receptor function.[10]
Mitochondrial diseases have a high prevalence of fatigue and debilitation, with the severity of disease predicting the level of fatigue; Gorman et al (2015) found the degree of muscle weakness was not related to fatigue severity.[11]
ME/CFS[edit | edit source]
There is increasing evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients.[12] Muscle biopsies have shown evidence of mitochondrial degeneration,[13] deletions of mitochondrial DNA,[14][15] the reduction of mitochondrial activity,[14] and Sarah Myhill found measurable mitochondrial dysfunction correlating with severity of illness.[16][17] Myhill also produced improvement by targeting those dysfunctions.[18] Mitochondrial DNA variants correlate with symptoms, symptom clusters & symptom severity.[19]
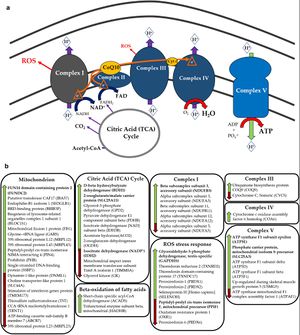
Green arrows show increases and red arrows show decreases.[12]
Source: Journal of Translational Medicine 18(1):365 Sweetman et al. 2020. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02533-3. PMC7512220.
A small study by Sweetman et al. (2020) found a large number of proteins were over or under expressed in ME/CFS patients compared to controls, with many of those proteins known to be involved in mitochondrial function, oxidative phosphorylation, electron transport chain complexes, and redox regulation. The study supported the model of deficient ATP production in ME/CFS, and also suggesting increased oxidative stress.[12]
Mitochondrial disorders can be mistaken for chronic fatigue syndrome.[20]
There is evidence of genetic risk factors for mitochondrial dysfunction in related diseases such as complex regional pain syndrome, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), and dysautonomia.[21]
A small study of 20 ME/CFS patients meeting the Canadian Consensus Criteria found that re-activation of Human Herpesvirus-6 caused mitochondria dysfunction and reduced the ATP content of cells.[22]
Notable studies[edit | edit source]
- 1991, Mitochondrial abnormalities in the postviral fatigue syndrome[13]
- 1995, Unusual pattern of mitochondrial DNA deletions in skeletal muscle of an adult human with chronic fatigue syndrome [15]
- 1996, Sensory characterization of somatic parietal tissues in humans with chronic fatigue syndrome[14]
- 1997, Chronic fatigue syndrome and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function[23]
- 2005, Targeting of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF to host mitochondria is essential for bacterial pathogenesis: critical role of the 16th leucine residue in EspF[10]
- 2009, Chronic fatigue syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction[17]
- 2009, Integrated cytokine and metabolic analysis of pathological responses to parasite exposure in rodents[8]
- 2009, Coenzyme Q10 deficiency in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is related to fatigue, autonomic and neurocognitive symptoms and is another risk factor explaining the early mortality in ME/CFS due to cardiovascular disorder[24]
- 2010, Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome performed worse than controls in a controlled repeated exercise study despite a normal oxidative phosphorylation capacity[25]
- 2010, Interactions between bacterial pathogens and mitochondrial cell death pathways[9]
- 2012, Mitochondrial dysfunction and the pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)[16]
- 2013, Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) - a clinical audit[18]
- 2013, Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and encephalomyelitis disseminata/multiple sclerosis show remarkable levels of similarity in phenomenology and neuroimmune characteristics.[26]
- 2013, Viruses as Modulators of Mitochondrial Functions[6]
- 2013, The role of mitochondrial dysfunctions due to oxidative and nitrosative stress in the chronic pain or chronic fatigue syndromes and fibromyalgia patients: peripheral and central mechanisms as therapeutic targets?[27]
- 2014, Metabolism in chronic fatigue syndrome[28]
- 2014, Mitochondrial dysfunctions in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome explained by activated immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways[29]
- 2015, Mitoprotective dietary approaches for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Caloric restriction, fasting, and ketogenic diets[30]
- 2015, Mitochondrial Myopathy in Follow-up of a Patient With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome[20]
- 2015, Increased prevalence of two mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in functional disease: Are we describing different parts of an energy-depleted elephant?[21]
- 2015, Metabolic profiling reveals anomalous energy metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in chronic fatigue syndrome patients[31]
- 2016, Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein cooperates with phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα to induce mitochondrial fragmentation[7]
- 2016, Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?[32]
- 2016, Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts[33]
- 2016, Mitochondrial DNA variants correlate with symptoms in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome[19]
- 2018, Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation[34]
- 2020, Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome[22] (Full text)
- 2020, An Isolated Complex V Inefficiency and Dysregulated Mitochondrial Function in Immortalized Lymphocytes from ME/CFS Patients[35] - (Full text)
- 2020, A SWATH-MS analysis of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome peripheral blood mononuclear cell proteomes reveals mitochondrial dysfunction[12] - (Full text)
Videos[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
- Cellular respiration
- Exercise
- Genetics
- Ketogenic diet
- Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS)
- NADH
- NT Factor
- Robert Naviaux
- Sarah Myhill
Learn more[edit | edit source]
- 2016, Immune System Conserves Energy By Altering Metabolism[38]
- 2016, ME Association to fund fourth study into the role of the mitochondria in ME/CFS[39]
- 2016, ME Association Goes All in on the Mitochondria in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)[40]
- 2016, Australian metabolomics study of young women with ME/CFS (CCC)[41]
- 2016, "Mitochondria Man Gets Money UK Goes Mega Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Research Moves Forward"[42]
Citations to add to text[edit | edit source]
Lodi1997 [23] Armstrong2015 [31] Craig2015[30] Felici2016[33] Ostojic2016 [32] Sliter2018 [34] Missailidis2020 [35].
Vermeulen2010 [25] Maes2009 [24] Morris2013 [26] Morris2014 [29] Armstrong2014 [28] Meeus2013 [27]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Yu, Chia-Yi (December 2009). "The Interferon Stimulator Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein Facilitates Cell Death by Disrupting the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and by Activating Caspases". Journal of Virology.
- ↑ Mukherjee, A (March 2011). "The coxsackievirus B 3C protease cleaves MAVS and TRIF to attenuate host type I interferon and apoptotic signaling". PLoS Pathology. 7.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Derakhshan, Mohammed (August 1, 2006). "Human herpesvirus 1 protein US3 induces an inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport". Journal of General Virology. 87: 2155–2159.
- ↑ Koundouris, A (May 2000). "Poliovirus Induces an Early Impairment of Mitochondrial Function by Inhibiting Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 271: 610–4.
- ↑ Ripoli, Maria (October 2009). "Hepatitis C Virus-Linked Mitochondrial Dysfunction Promotes Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α-Mediated Glycolytic Adaptation". Journal of Virology.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Anand, Sanjeev K; Tikoo, Suresh K (October 24, 2013), "Viruses as Modulators of Mitochondrial Functions", Advances in Virology, Advances in Virology, 2013: 738794, doi:10.1155/2013/738794
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Siu, GK; Zhou, F; Yu, MK; Zhang, L; Wang, T; Liang, Y; Chen, Y; Chan, HC; Yu, S (March 2016), "Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein cooperates with phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα to induce mitochondrial fragmentation", Sci. Rep., doi:10.1038/srep23464, PMID 27010100
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Saric, J; Li, JV; Swann, JR; et al. (November 8, 2010), "Integrated cytokine and metabolic analysis of pathological responses to parasite exposure in rodents" Check
|url=value (help), Journal of proteome research, 9: 2255–2264 - ↑ 9.0 9.1 Rudel T, T; Kepp O, O; Kozjak-Pavlovic V, V (October 2010), "Interactions between bacterial pathogens and mitochondrial cell death pathways", Nat Rev Microbiol., doi:10.1038/nrmicro2421, PMID 20818415
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Nagai, T; Abe, A; Sasakawa, C (January 2005), "Targeting of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF to host mitochondria is essential for bacterial pathogenesis: critical role of the 16th leucine residue in EspF", J Bio. Chem., doi:10.1074/jbc.M411550200, PMID 15533930
- ↑ Gorman, Grainne S.; Elson, Joanna L.; Newman, Jane; Payne, Brendan; McFarland, Bobby; Newton, Julia L.; Turnbull, Doug M. (2015). "Perceived fatigue is highly prevalent and debilitating in patients with mitochondrial disease". Neuromuscular Disorders. 25 (7): 563–566. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2015.03.001.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Sweetman, Eiren; Kleffmann, Torsten; Edgar, Christina; de Lange, Michel; Vallings, Rosamund; Tate, Warren (September 24, 2020). "A SWATH-MS analysis of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome peripheral blood mononuclear cell proteomes reveals mitochondrial dysfunction". Journal of Translational Medicine. 18 (1): 365. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02533-3. ISSN 1479-5876. PMC 7512220.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Behan, WMH; More, IAR; Behan, PO (1991), "Mitochondrial abnormalities in the postviral fatigue syndrome", Acta Neuropathologica, 83 (1): 61–65, PMID 1792865
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Vecchiet, L; Montanari, G; Pizzigallo, E; et al. (April 19, 1996), "Sensory characterization of somatic parietal tissues in humans with chronic fatigue syndrome", Neuroscience Letters, 208 (2): 117–120, PMID 8859904
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Zhang, C; Baumer, A; Mackay, IR; et al. (April 1995), "Unusual pattern of mitochondrial DNA deletions in skeletal muscle of an adult human with chronic fatigue syndrome", Human Molecular Genetics, 4 (4): 751–754, PMID 7633428
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Booth, NE; Myhill, S; McLaren-Howard, J (2012), "Mitochondrial dysfunction and the pathophysiology of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)", Int J Clin Exp Med, 5 (3): 208–220, PMID 22837795
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Myhill, S; Booth, NE; McLaren-Howard, J (January 15, 2009), "Chronic fatigue syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction", Int J Clin Exp Med, 2 (1): 1–16, PMID 19436827
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Myhill, Sarah; Booth, Norman E; McLaren-Howard, John (2013), "Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in the treatment of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) - a clinical audit.", International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, PMID 23236553
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Billing-Ross, Paul; Germain, Arnaud; Ye, Kaixiong; et al. (2016), "Mitochondrial DNA variants correlate with symptoms in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome", Journal of Translational Medicine, 14: 19, doi:10.1186/s12967-016-0771-6, ISSN 1479-5876, PMID 26791940, lay summary
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Galán, Fernando; de Lavera, Isabel; Cotán, David; Sánchez-Alcázar, José A (September 24, 2015), "Mitochondrial Myopathy in Follow-up of a Patient With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome", J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep, 3 (3), doi:10.1177/2324709615607908, PMID 26904705
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Boles, RG; Zaki, EA; Kerr, JR; et al. (July 2015), "Increased prevalence of two mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in functional disease: Are we describing different parts of an energy-depleted elephant?", Mitochondrion, 23: 1-6, doi:10.1016/j.mito.2015.04.005, PMID 25934187
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Schreiner, Philipp; Harrer, Thomas; Scheibenbogen, Carmen; Lamer, Stephanie; Schlosser, Andreas; Naviaux, Robert K.; Prusty, Bhupesh K. (April 1, 2020). "Human Herpesvirus-6 Reactivation, Mitochondrial Fragmentation, and the Coordination of Antiviral and Metabolic Phenotypes in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome". ImmunoHorizons. 4 (4): 201–215. doi:10.4049/immunohorizons.2000006. ISSN 2573-7732. PMID 32327453.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Lodi, R.; Taylor, D. J.; Radda, G. K. (1997). "Chronic fatigue syndrome and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function". Muscle & Nerve. 20 (6): 765–766. ISSN 0148-639X. PMID 9149090.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Maes, M; Mihaylova, I; Kubera, M; Uytterhoeven, M; Vrydags, N; Bosmans, E (2009), "Coenzyme Q10 deficiency in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is related to fatigue, autonomic and neurocognitive symptoms and is another risk factor explaining the early mortality in ME/CFS due to cardiovascular disorder", Neuro Endocrinol Lett., PMID 20010505
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Vermeulen, RC; Kirk, RM; Visser, FC; Sluiter, W; Scholte, HR (October 2010), "Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome performed worse than controls in a controlled repeated exercise study despite a normal oxidative phosphorylation capacity", Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/1479-5876-8-93, PMID 20937116
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Morris, G; Maes, M (September 2013), "Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and encephalomyelitis disseminata/multiple sclerosis show remarkable levels of similarity in phenomenology and neuroimmune characteristics.", BMC Med, doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-205, PMID 24229326
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Meeus, M; Nijs, J; Hermans, L; Goubert, D; Calders, P (September 2013), "The role of mitochondrial dysfunctions due to oxidative and nitrosative stress in the chronic pain or chronic fatigue syndromes and fibromyalgia patients: peripheral and central mechanisms as therapeutic targets?", Expert Opin Ther Targets, doi:10.1517/14728222.2013.818657, PMID 23834645
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Armstrong, CW; McGregor, NR; Butt, HL; Gooley, PR (October 2014), "Metabolism in chronic fatigue syndrome", Adv Clin Chem, 66: 121-72, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801401-1.00005-0, PMID 25344988
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Morris, Gerwyn; Maes, Michael (March 2014), "Mitochondrial dysfunctions in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome explained by activated immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways", Metab Brain Dis., doi:10.1007/s11011-013-9435-x, PMID 24557875
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Craig, Courtney (November 2015), "Mitoprotective dietary approaches for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Caloric restriction, fasting, and ketogenic diets", Medical Hypotheses, 85 (5): 690-693, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2015.08.013, PMID 26315446
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Armstrong, Christopher W.; McGregor, Neil R.; Lewis, Donald P.; Butt, Henry L.; Gooley, Paul R. (May 22, 2015). "Metabolic profiling reveals anomalous energy metabolism and oxidative stress pathways in chronic fatigue syndrome patients" (PDF). Metabolomics. 11: 1626–1639. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help) - ↑ 32.0 32.1 Ostojic, Sergej M. (August 1, 2016). "Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a myth or reality?". Clinical Science (Lond.). 130 (16): 1407–1416. doi:10.1042/CS20160200. ISSN 1470-8736. PMID 27389587.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Felici, Roberta; Lapucci, Andrea; Cavone, Leonardo; Pratesi, Sara; Berlinguer-Palmini, Rolando; Chiarugi, Alberto (2015). "Pharmacological NAD-Boosting Strategies Improve Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Human Complex I-Mutant Fibroblasts". Molecular Pharmacology. 87 (6): 965–971. doi:10.1124/mol.114.097204. ISSN 1521-0111. PMID 25788480.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Sliter, Danielle A.; Martinez, Jennifer; Hao, Ling; Chen, Xi; Sun, Nuo; Fischer, Tara D.; Burman, Jonathon L.; Li, Yan; Zhang, Zhe (August 22, 2018). "Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0448-9. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Missailidis, Daniel; Annesley, Sarah; Allan, Claire; Sanislav, Oana; Lidbury, Brett; Lewis, Don; Fisher, Paul (February 6, 2020). "An Isolated Complex V Inefficiency and Dysregulated Mitochondrial Function in Immortalized Lymphocytes from ME/CFS Patients". Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (3): 1074. doi:10.3390/ijms21031074. PMC 7036826. PMID 32041178.
- ↑ Andersen, Paul (May 5, 2016). "Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell". YouTube. Bozeman Science. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help) - ↑ "CFS - The Central Cause: Mitochondrial Failure - DoctorMyhill". www.drmyhill.co.uk. Retrieved September 6, 2018.
- ↑ Marker, Kara (July 10, 2016). "Immune System Conserves Energy By Altering Metabolism". LabRoots. Retrieved September 6, 2018. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help) - ↑ "ME Association to fund fourth study into the role of the mitochondria in ME/CFS | 10 March 2016". www.meassociation.org.uk. Retrieved September 6, 2018.
- ↑ Morten, Karl (March 2016). "ME Association Goes All in on the Mitochondria in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)". Health Rising's Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) and Fibromyalgia Forums. Retrieved September 6, 2018. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help) - ↑ Nimmo, Sasha (July 6, 2016). "Australian metabolomics study of young women with ME/CFS (CCC)". ME Australia. Retrieved September 6, 2018. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help) - ↑ Johnson, Cort (May 19, 2016). "The Mitochondria Man Gets His Money and The UK Goes MEGA: ME/CFS Research Moving Forward - Health Rising". Health Rising. Retrieved September 6, 2018. Cite has empty unknown parameter:
|dead-url=(help)