Portal:Energy metabolism/Selected article
- These are selected articles related to Energy metabolism which appear on Portal:Energy metabolism.
Post-exertional malaise (PEM) is a worsening of many ME/CFS symptoms as a result of physical or mental exertion. Patients, ME/CFS organizatons, clinicians and researchers that work in the ME/CFS field often referred to it as "the marker," i.e., the main symptom that differentiates ME and CFS from other fatiguing illnesses. PEM can last for days to weeks after the exertion. (more...)
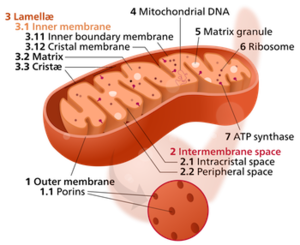
The Citric acid cycle/Krebs cycle/TCA cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions that form a key part of aerobic respiration in cells. This work takes place inside the mitochondria. (more...)
The Energy Envelope Theory is a self-management tool to reduce symptom severity and the frequency of relapses. This theory suggests that because variations in day-to-day energy levels are often unpredictable in people with ME/CFS, they are to assess their perceived energy levels on a daily basis (or in smaller time increments, as needed) and use that level to gauge their energy expenditure for the day. It encourages people with ME/CFS to accept their daily energy limitations and not exceed or fight them. (more...)
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is an enzyme that is part of the citric acid cycle. It catalyzes the reaction that transforms pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. A large study by Fluge and Mella of 200 patients meeting the Canadian Consensus Criteria and 102 controls found a pattern of amino acids that suggested functional impairment of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), supported by increased mRNA expression of the inhibitory PDH kinases 1, 2, and 4; sirtuin 4; and PPARδ in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from both sexes. (more...)
Two-day cardiopulmonary exercise testing or 2-day CPET is a ...of post-exertional malaise (PEM), one of the cardinal symptoms that distinguishes between individuals with and without ME/CFS. The hypothesis is that ME/CFS patients are almost unique in having a severe deterioration in the second of the two cardiopulmonary exercise tests performed on consecutive days. The test is also frequently used in research to compare outcomes pre- and post- exercise. (more...)

