Stem cell therapy
From MEpedia, a crowd-sourced encyclopedia of ME and CFS science and history
(Redirected from Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy)
This article is a stub. |
Stem cell therapy, in particular the use of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) is a potential treatment that has been suggested for ME/CFS.[1]
Theory
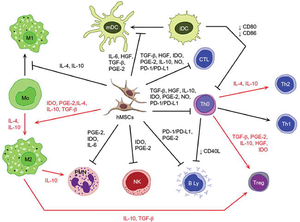
HGF, hepatocyte growth factor;
TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β;
PGE-2, prostaglandin E2; IDO, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase;
NO, nitric oxide; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1;
hMSC, human mesenchymal stem cell;
Treg, T regulatory; Th, T helper cell
CTL, cytotoxic T cell; mDC, mature dendritic cell
PD-1, programmed cell death protein ;1
PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocyte;
NK, Natural killer cell
Evidence
Clinical trials of stem cell therapies have not yet been published.[1]
Clinicians
Risks and safety
Costs and availability
See also
- Immune system
- Metabolic trap
- Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase
- Interleukin
- transforming growth factor-β;
- Nitric oxide
- T regulatory
- T helper cell
- Cytotoxic T cell
- Natural killer cell
Learn more
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Moreno-Manzano, Victoria; García, Elisa Oltra (November 5, 2018). "Culturing Adult Stem Cells for Cell-Based Therapeutics: Neuroimmune Applications". Cell Culture. IntechOpen. doi:10.5772/intechopen.80714.

