Anaerobic and aerobic metabolism
Anaerobic metabolism and aerobic metabolism (anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration) are the two methods of generating energy in the human body, including converting food sources into energy for exercise, mental activity and physical activity.[1]
Aerobic respiration[edit | edit source]
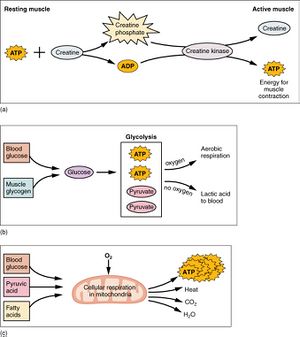
Source: Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas.[2]
Aerobic respiration is also known as cellular respiration.[2]
Anaerobic exercise[edit | edit source]
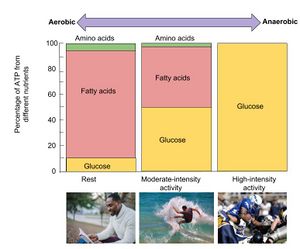
Anaerobic exercise is high-intensity exercise that is meant to be very short (10 to 15 seconds) and fast/powerful, and usually can't be sustained for long. Typically the exercise is then repeated after a short rest.[3] The word "anaerobic" means without oxygen, instead of using oxygen to keep muscles going, the energy already stored in the muscles is used, known as glycogen.[3]

Examples include:
- Resistance training, like using gym machines with weights
- Very short sprints
- Weight lifting[3]
Aerobic exercise[edit | edit source]
Aerobic exercise is "cardiovascular conditioning ("cardio") that strengthens both your heart and lungs, using continuous movements.[3] The word aerobic means "with oxygen," aerobic exercise is fueled by the oxygen from breathing, which means it can be carried out for an extended period of time.[3]
Examples include:
- Running or jogging
- Walking at a brisk pace
- Swimming
- Rowing
- Cycling
- Step aerobics or aqua aerobics
- Using cardio machines like an elliptical or stair climber[3]
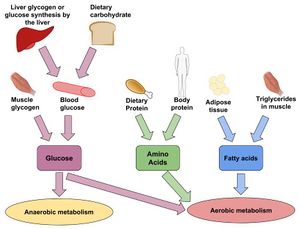
Energy sources and processes[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Learn more[edit | edit source]
- Chapter 10b -Fuel sources for exercise - OpenOregon Press
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Callahan, Alice; Leonard, Heather; Powell, Tamberly (October 14, 2020). "10b -Fuel sources for exercise". Nutrition: Science and Everyday Application. ISBN 978-1-63635-003-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas. Retrieved January 28, 2022.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Difference between aerobic and anaerobic exercise". WebMD. 2021. Retrieved January 28, 2022.

