Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Author: CDC
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 or SARS-CoV-2, commonly known as the novel coronavirus 2019, is the virus that causes the COVID-19 infectious respiratory disease.[1] SARS-CoV-2 was previously known as n-2019-nCoV.[1][2][3][4]
SARS-CoV-2 was first identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, as a result of investigations into a group of patients with the newly discovered COVID-19 pneumonia.[1] SARS-CoV-2 can cause COVID-19 in babies, children, and adults of any age.[5] It spread globally, and the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a pandemic on March 11, 2020.[6][7]
COVID-19
Some people who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 do not develop COVID-19 illness, but these asymptomatic carriers can transmit it to others.[1] Of those who do develop COVID-19, 1 in 6 people need medical help, and the 2019-2021 pandemic has caused a significant number of deaths.[1][8][9]

Coronaviruses, including the viruses that cause COVID-19, SARS, H1N1 flu (swine flu), and seasonal flu, are all protected by an envelope of fat; soap molecules invade the envelope and disrupt its integrity. High concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol can strip away parts of the envelope, leading to the inaction of of the viral molecules.[10][11] Isopropyl alcohol works against all viruses enveloped in fat, and ethyl alcohol additionally works against some non-enveloped viruses such as rotaviruses, when used at the correct concentrations.[10]
Comparison with SARS and influenza
Author: Dietz et al (2020), mSystems 5:e00245-20.
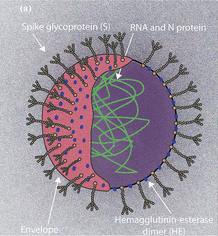
The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 illness is closely related to SARS-CoV: the coronavirus that causes Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.[12] The genome of the SARS-COV-2 virus was found to have 82% similarity with the virus that causes SARS.[12]
The SARS-CoV-2 virus appears to be significantly more contagious than the SARS-CoV virus that causes SARS, and spreads significantly in the community, unlike SARS-CoV which spread more in hospitals, healthcare settings and nursing homes than in the wider community.[13][14]
The resulting COVID-19 illness has a lower risk of death than SARS, but has killed a much higher number of people.[15][16] Both COVID-19 and SARS are many times more likely to kill than seasonal flu illnesses.[17][18] COVID-19 also has a much longer incubation period than the flu, so people may infect others before they are aware they are ill.[17]
Notable studies
- 2020, Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2 - (Full text)
Learn more
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) - CDC
- Coronavirus - World Health Organization
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Pandemic - World Health Organization
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) - NHS
COVID-19 vs Flu: Similarities and Differences
- Similarities and Differences between Flu and COVID-19 - CDC
- Similarities and differences between COVID-19 and Influenza - World Health Organization
- Why living with Covid would not be the same as flu - The Guardian, UK
See also
- COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 19)
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
- Viral testing in ME/CFS
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 World Health Organization (2020). "Q&A on coronaviruses (COVID-19)". World Health Organization. Retrieved March 16, 2020.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (February 27, 2020). "Human Coronavirus Types". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved March 16, 2020.
- ↑ Li, Guangdi; Clercq, Erik De (March 2020). "Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 19 (3): 149–150. doi:10.1038/d41573-020-00016-0.
- ↑ "Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it". World Health Organization. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ↑ Wei, Min; Yuan, Jingping; Liu, Yu; Fu, Tao; Yu, Xue; Zhang, Zhi-Jiang (February 14, 2020). "Novel Coronavirus Infection in Hospitalized Infants Under 1 Year of Age in China". JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2131.
- ↑ Hui, David S.; Azhar, Esam I.; Madani, Tariq A.; Ntoumi, Francine; Kock, Richard; Dar, Osman; Ippolito, Giuseppe; Mchugh, Timothy D.; Memish, Ziad A. (February 1, 2020). "The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health — The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 91: 264–266. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. ISSN 1201-9712. PMID 31953166.
- ↑ "WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020". World Health Organization. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ↑ CDC (March 20, 2020). "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) – Symptoms". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved March 24, 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Chemical Disinfectants | Disinfection & Sterilization Guidelines | Guidelines Library | Infection Control". Centers for Disease Control. April 4, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2021.
- ↑ Jabr, Ferris (March 13, 2020). "Why Soap Works". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 11, 2021.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Chan, Jasper Fuk-Woo; Kok, Kin-Hang; Zhu, Zheng; Chu, Hin; To, Kelvin Kai-Wang; Yuan, Shuofeng; Yuen, Kwok-Yung (2020). "Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan". Emerging Microbes & Infections. 9 (1): 221–236. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. ISSN 2222-1751. PMC 7067204. PMID 31987001.
- ↑ Liu, Ying; Gayle, Albert A.; Wilder-Smith, Annelies; Rocklöv, Joachim (March 2020). "The reproduction number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavidus". Journal of Travel Medicine. 27 (2). doi:10.1093/jtm/taaa021. PMC 7074654. PMID 32052846.
- ↑ Wilder-Smith, Annelies; Chiew, Calvin J.; Lee, Vernon J. (May 1, 2020). "Can we contain the COVID-19 outbreak with the same measures as for SARS?". The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 20 (5): e102–e107. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30129-8. ISSN 1473-3099. PMID 32145768.
- ↑ "SARS | Frequently Asked Questions |". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. February 8, 2019. Retrieved May 10, 2020.
- ↑ "COVID-19 Map". Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Retrieved May 10, 2020.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Rettner, Rachael (April 30, 2020). "How does the new coronavirus compare with the flu?". Live Science. Retrieved May 10, 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization (March 17, 2020). "Q&A: Similarities and differences – COVID-19 and influenza". World Health Organization. Retrieved May 10, 2020.

