Musculoskeletal system
From MEpedia, a crowd-sourced encyclopedia of ME and CFS science and history
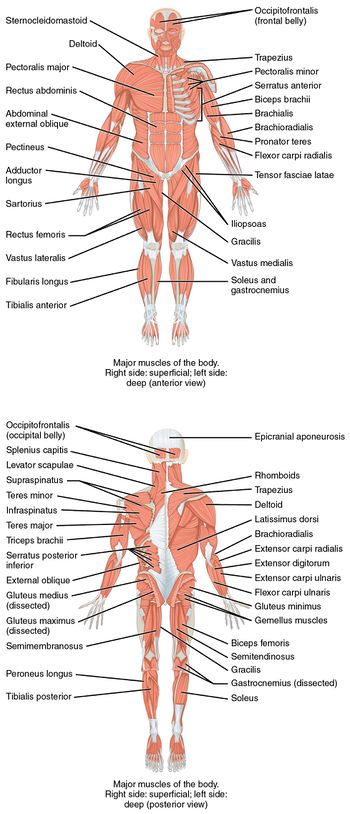
Source: Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "11.2 Naming Skeletal Muscles". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas.[1]
The musculoskeletal system "includes the bones of the skeleton and the cartilages, ligaments, and other connective tissue that stabilize or connect the bones. In addition to supporting the weight of the body, bones work together with muscledddds to maintain body position and to produce controlled, precise movements. Without the skeleton to pull against, contracting muscle fibers could not make us sit, stand, walk, or run."[2]
Bones
206 bones perform 5 functions:
- provide support for the body
- store minerals and lipids (fats)
- produce blood cells
- protect body organs
- provide leverage and movement[2]
Other elements
- joints
- tendons
- ligaments
- skeletal muscless
- nerves
- cartilage
- hyaline cartilage
- elastic cartlilage
- fibrocartilage[2]
Musculoskeletal disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are conditions that can affect your muscles, bones, and joints. They include conditions such as:
- Tendinitis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Bone fractures[3]
See also
Learn more
- 2014, Musculoskeletal System Overview By Mr. Kish's Science Channel
References
- ↑ Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "11.2 Naming Skeletal Muscles". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas. Retrieved January 29, 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Musculoskeletal System | Cleveland Clinic". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved August 25, 2018.
- ↑ Cherney, Kristeen (March 21, 2018). "Musculoskeletal Disorders: Definition and Patient Education". Healthline. Retrieved August 25, 2018.

