Leucocyte
From MEpedia, a crowd-sourced encyclopedia of ME and CFS science and history
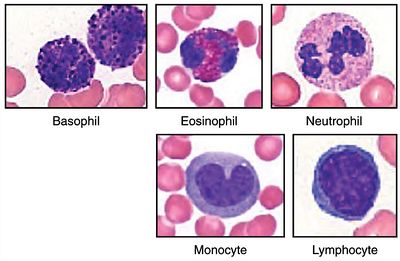
Leucocytes or leukocytes, colloquially known as white blood cells (WBCs), are clear, colorless cells that circulate in the blood and lymph and are integral part of the immune system.[1]
Leucocytes are divided into the types: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes. Each of these types has further derivatives, for example Natural killer cells are derivative of lymphocytes.[2]
There are two lymphoid tissue types:bibideebeepbop
- Primary Lymphoid tissues, comprising the bone marrow and thymus where leucocytes are synthesized[3]
- Secondary lymphoid tissues, comprising the spleen, lymph nodes and mucosa associated lymphoid tissues (MALT)[3]
Secondary lymphoid tissues contain the mature leucocytes that react to infection, triggering an immune response[3].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ "leucocyte". The Free Dictionary.
- ↑ "Natural Killer Cells | British Society for Immunology". immunology.org. Retrieved October 9, 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Male, D (2007), Immunology, Milton Keynes, The Open University/Milton Keynes, The Open University

