Methionine
From MEpedia, a crowd-sourced encyclopedia of ME and CFS science and history
(Redirected from L-methionine)
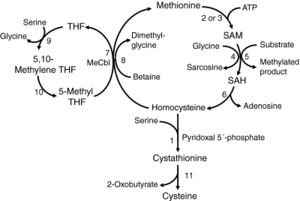
Key
SAM: S-adenosylmethionine (SAM-e)
SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine
THF: tetrahydrofolate
MeCbl: methylcobalamin
1. Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS)
2. methionine adenosyltransferase I/III
3. methionine adenosyltransferase II
4. glycine N-methyltransferase
5. numerous methyltransferases
6. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
7. methionine synthase
8. betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase
9. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
10. methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
11. cystathionine gamma-lyase
Methionine or l-methionine is the only sulfur-containing essential amino acid.[1]
Purpose[edit | edit source]
Methionine is a pre-cursor to creatine.[1]
Sources[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
- Methylation cycle
- Energy metabolism
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Arginine
- Cystathionine beta synthase (CBS)
- Serine
- Amy Yasko
Learn more[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 van der Poll, MCG; Luiking, YC; Dejong, CHC; Soeters, PB (September 2, 2009). "Amino Acids". In Caballero, Benjamin (ed.). Guide to Nutritional Supplements. Oxford, UK: Academic Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-12-375661-9.

