File:Turmeric and curcurmin.jpg
Original file (6,414 × 3,657 pixels, file size: 885 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary[edit | edit source]
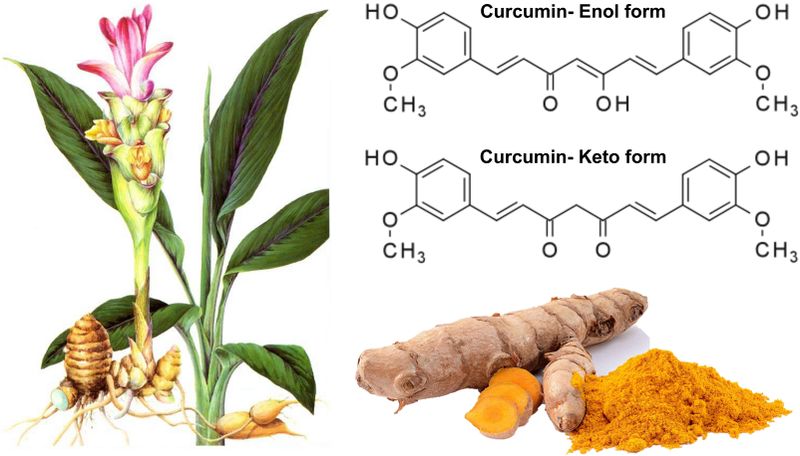
The molecular structure of curcumin isolated from the root of turmeric. Curcumin, a natural compound, is the most active agent of the polyphenolic curcuminoids derived from the root of turmeric (Curcuma longa). It is a tautomeric compound existing in organic solvents as its enolic form, and in water as a keto form. Turmeric, as a member of the ginger family, has been widely used as an herbal medicine, ingredient of cosmetics, and dietary supplement.
Source: Front. Pharmacol., 09 May 2018 doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00472 Fig 1. Curcumin, A Polyphenolic Curcuminoid With Its Protective Effects and Molecular Mechanisms in Diabetes and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00472/full License: CC-BY-4.0
Licensing[edit | edit source]
 |
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. | |
|
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 19:19, October 1, 2018 |  | 6,414 × 3,657 (885 KB) | Notjusttired (talk | contribs) | The molecular structure of curcumin isolated from the root of turmeric. Curcumin, a natural compound, is the most active agent of the polyphenolic curcuminoids derived from the root of turmeric (Curcuma longa). It is a tautomeric compound existing in o... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 4 pages use this file:

