Cystathionine beta synthase
From MEpedia, a crowd-sourced encyclopedia of ME and CFS science and history
This article is a stub. |
Cystathionine Beta Synthase or CBS is an enzyme in the methionine catabolic pathway.[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
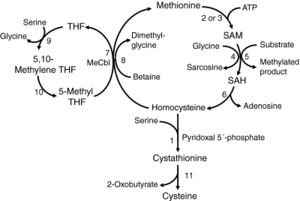
Methionine metabolic pathways
Key
SAM: S-adenosylmethionine (SAM-e)
SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine
THF: tetrahydrofolate
MeCbl: methylcobalamin
1. Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS)
2. methionine adenosyltransferase I/III
3. methionine adenosyltransferase II
4. glycine N-methyltransferase
5. numerous methyltransferases
6. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
7. methionine synthase
8. betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase
9. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
10. methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
11. cystathionine gamma-lyase
Key
SAM: S-adenosylmethionine (SAM-e)
SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine
THF: tetrahydrofolate
MeCbl: methylcobalamin
1. Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS)
2. methionine adenosyltransferase I/III
3. methionine adenosyltransferase II
4. glycine N-methyltransferase
5. numerous methyltransferases
6. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
7. methionine synthase
8. betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase
9. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
10. methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
11. cystathionine gamma-lyase
CBS deficiency[edit | edit source]
CBS deficiency is rare and physical signs commonly associated with it are:
- eye lens dislocated (ectopia lentis) and/or severe short-sighted vision
- being very tall, with long limbs similar to in Marfan's syndrome, osteoporosis and bone deformities (e.g., pectus excavatum or carinatum, genu valgum and scoliosis)
- intellectual disability or developmental delay, seizures, psychiatric and behavioural problems and extrapyramidal signs
- Vascular system: blood clots moving to obstruct blood vessels (thromboembolism)[1]
ME/CFS[edit | edit source]
Notable studies[edit | edit source]
- 2017, Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency[1] (Full text)
See also[edit | edit source]
Learn more[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Morris, Andrew A.M.; Kožich, Viktor; Santra, Saikat; Andria, Generoso; Ben-Omran, Tawfeg I.M.; Chakrapani, Anupam B.; Crushell, Ellen; Henderson, Mick J.; Hochuli, Michel (2017). "Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 40 (1): 49–74. doi:10.1007/s10545-016-9979-0. ISSN 0141-8955. PMC 5203861. PMID 27778219.

