File:Cellular-respiration.jpg
Original file (902 × 1,014 pixels, file size: 319 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Title[edit | edit source]
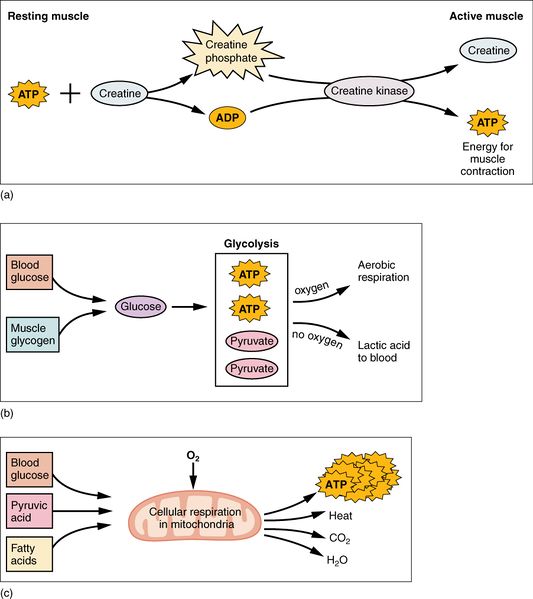
Muscle metabolism including creatine, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), aerobic respiration, oxygen, pyruvate, blood glucose, muscle glycogen, lactic acid, pyruvic acid, and essential fatty acids.
Summary[edit | edit source]
Aerobic respiration, also known as cellular respiration, is the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Approximately 95% of the ATP required for resting or moderately active muscles is provided by aerobic respiration, which takes place in mitochondria.
Author:[edit | edit source]
Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas. Retrieved January 28, 2022.[1]
Source[edit | edit source]
10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation, OpenStax.
Cite this as:
Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas.[1]
Licensing[edit | edit source]
 |
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. | |
|
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Betts, JG; Young, KA; Wise, JA; Johnson, E; Poe, B; Kruse, DH; Korol, O; Johnson, JE; Womble, M; DeSaix, P (April 25, 2013). "10.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation". Anatomy and Physiology. OpenStax. Houston, Texas. Retrieved January 28, 2022.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 09:33, July 29, 2019 |  | 902 × 1,014 (319 KB) | Notjusttired (talk | contribs) | Aerobic respiration, also known as cellular respiration, is the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Approximately 95 percent of the ATP required for resting or moderately active muscles is prov... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file:

