Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune diseases arise from an abnormal immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body.
Types of autoimmune diseases[edit | edit source]
Autoimmune diseases can be localized, which means affecting only specific tissues or organs, or systematic, making affecting many tissues or organs.[1]
Localized autoimmune disease[edit | edit source]
Examples include:
- Crohn's disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Graves' disease, which is one of the most common causes of thyroiditis[1]
Systemic autoimmune diseases[edit | edit source]
Examples include:
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Scleroderma
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus)[1]
Autoimmune hypothesis in ME and CFS[edit | edit source]
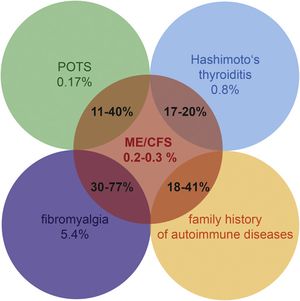
Many people with ME/CFS also have autoimmune conditions such as Fibromyalgia or Hashimoto's thyroiditis, or have a family history of autoimmune diseases.[2] POTS, or postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, can be initiated or maintained by autoantibodies as well, and POTS is common in people with ME. A number of different immune system abnormalities have been found in some patients with ME/CFS.[2]
ME/CFS is being investigated to determine if it is caused by Autoimmunity in some patients.
Notable studies[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Learn more[edit | edit source]
- Autoimmunity- British Society for Immunology
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 British Society for Immunology (March 2016). "Autoimmunity" (PDF). Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sotzny, Franziska; Blanco, Julià; Capelli, Enrica; Castro-Marrero, Jesús; Steiner, Sophie; Murovska, Modra; Scheibenbogen, Carmen (2018), "Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome – Evidence for an autoimmune disease", Autoimmunity Reviews, 17 (6): 601-609, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2018.01.009